Research group - G. Stirnimann
Detoxification processes
Role of the liver in adverse drug effects
The liver, rich in detoxifying enzymes, is the central metabolic organ of the human organism and plays a decisive part in the detoxification of ingested foreign substances such as alcohol, nicotine and medicinal drugs.
Without chemical change by the enzyme machinery of the liver, many drugs and environmental toxins could not be detoxified and eliminated from the body.
By largely determining the concentration of active substances in the target organ, the liver regulates to a great extent the effect of duration of action and side effects of many drugs.
If the liver function - whether as a result of liver disease as a whole or whether as a result of genetic variants or concomitant medication - is completely or partially limited, the efficiency- or side-effects profile can change, an important point which has to be considered by the prescribing doctors.
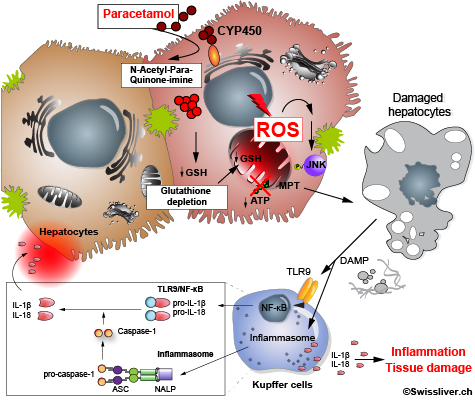
The liver, being the first organ to be exposed to foreign substances, detoxifies these substances but can also – paradoxically - render them more toxic. Hence, the liver is often the object of undesired side- effects of administered medications, potentially leading to liver failure.
Many medications had to be withdrawn from the market owing to damage to the liver often with fatal results. The research group is focussed on the metabolism of medications and the mechanisms which cause certain medications to lead to unforeseen and severe liver cell damage. The research group’s main concern is with the factors which detoxify toxic metabolites and other exogenous substances and with the mechanisms which can -in some patients- lead to a collapse of the defence front against toxic metabolic products. A better understanding of these detoxification processes will make it possible to develop even safer medication.

Research Focus
Detoxifying enzyme
Xenobiotic
Side-effects
Metabolism of medications
Liver damage
Detoxification processes
Research ratios
Humans : Animals
3 : 0
Top Major MeSH Headings
Metabolic Detoxification
Non-Narcotic Analgesics
Metabolic Clearance Rate
Cytochrome Reductases
Innate Immunity
Heart Failure
Iron
Drug-Induced Liver Injury
Liver injury caused by drugs: an update

ACG-guidelines- Management of Idiosyncratic DILI

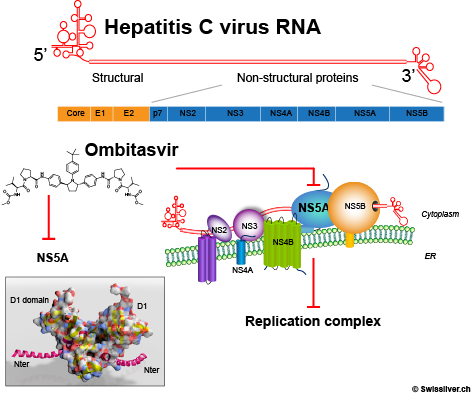
Reference PDB id: 1ZH1,
Reference to a novel dimeric form of NS5A domain I PDB id: 3FQQ
Publications :
Liver injury caused by drugs: an update-Stirnimann G et al., 2010- Swiss Med WklyOmbitasvir (ABT-267), a novel NS5A inhibitor for the treatment of hepatitis C- Stirnimann G., 2014 - Expert Opin Pharmacother.
